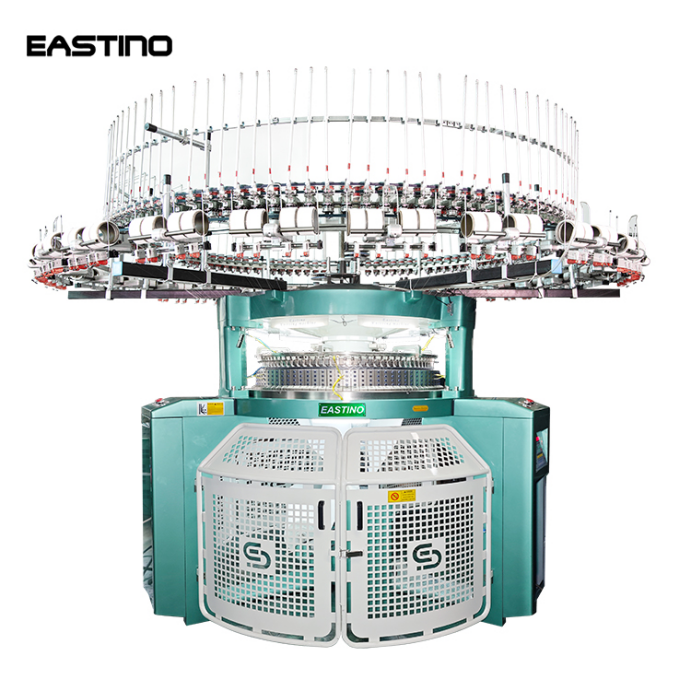
Whether you're a hobbyist, small batch designer, or textile start up, mastering a circular knitting machine is your ticket to fast, seamless fabric production. This guide walks you through using one step by step—perfect for both beginners and pros upgrading their craft.
Here’s what you’ll cover:
Understand how these machines work
Choose the right model, gauge, and yarn
Set up and thread your machine
Run a test swatch
Troubleshoot common issues
Maintain your machine
Scale up your knitting workflow
1. Understanding Circular Knitting Machines
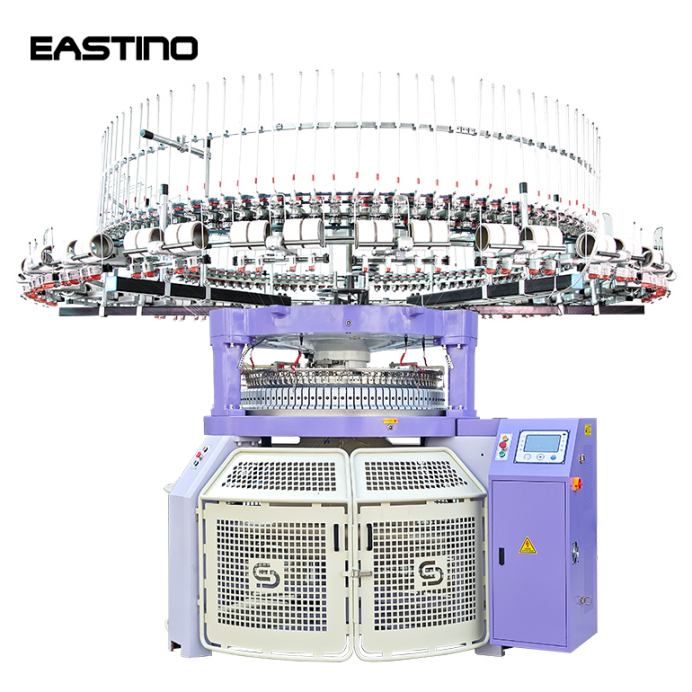

What are they?
A circular knitting machine uses a rotating needle cylinder to knit seamless tubes of fabric. You can produce anything from fitted beanies to large tubular panels. Unlike flatbed machines, circular units are faster and ideal for cylindrical products.
Why use one?
Efficiency: Knits continuous fabric up to 1,200 RPM
Consistency: Uniform stitch tension and structure
Versatility: Supports ribs, fleece, jacquard, and mesh
Scalability: Run multiple styles with minimal rethreading
LSI Keywords: knitting technology, fabric machine, textile machinery
2. Choosing the Right Machine, Gauge & Yarn
Gauge (Needles per Inch)
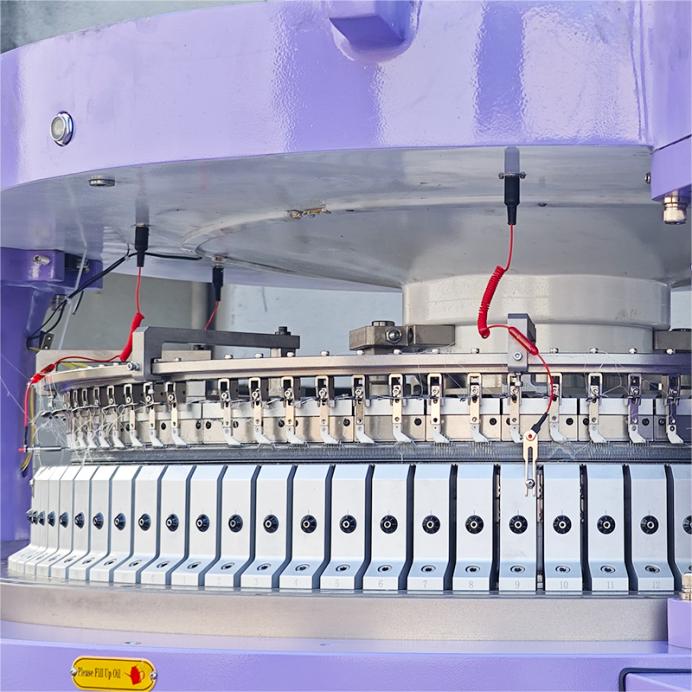

E18–E24: Everyday knit fabrics
E28–E32: Fine-gauge tees, gloves, ski hats
E10–E14: Chunky hats, upholstery fabric
Diameter
7–9 inches: Common for adult beanies
10–12 inches: Large hats, small scarves
>12 inches: Tubing, industrial usage
Yarn Selection
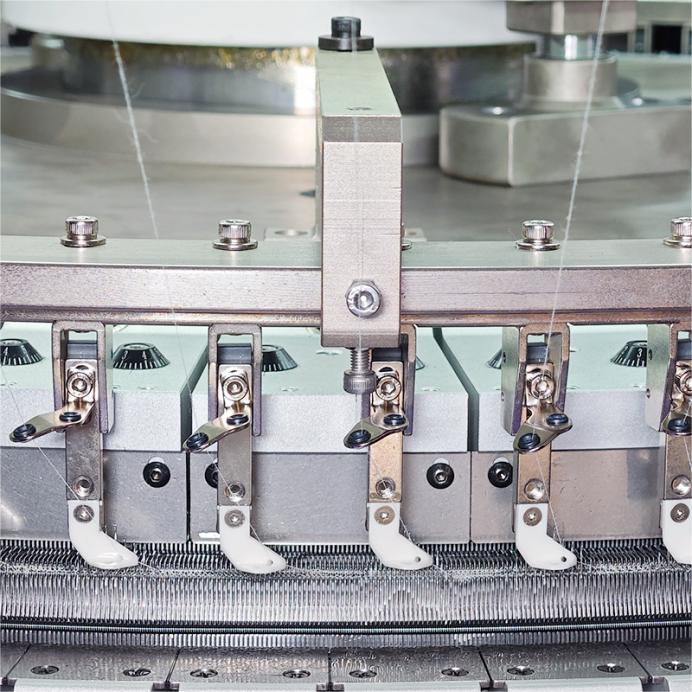

Fiber type: Acrylic, wool, or polyester
Weight: Worsted for structure, bulky for insulation
Care: Machine-friendly blends for easy maintenance
3. Setting Up and Threading Your Machine
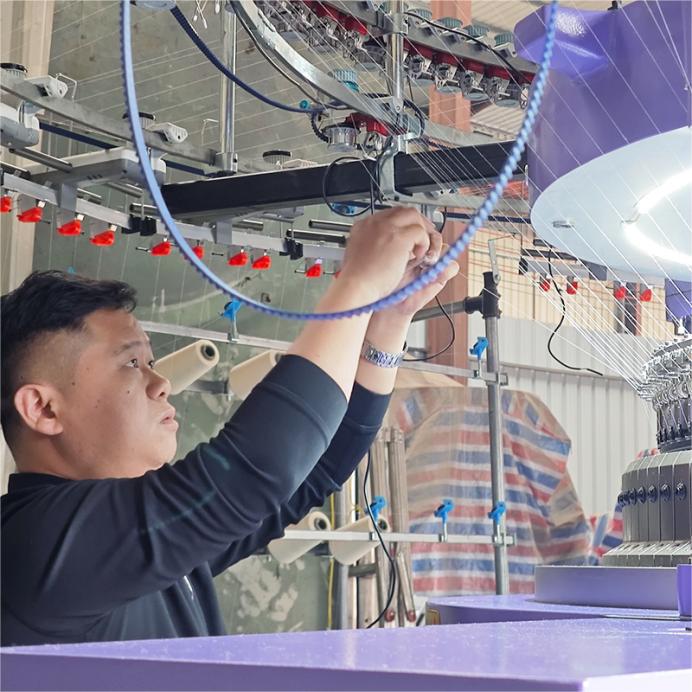

Follow these steps for foolproof setup:
A. Assemble and Level
Ensure sturdy table and machine bolted to work surface
Align cylinder level; misalignment can cause tension issues
B. Thread Yarn
Route yarn from cone → tension disk → eyelet
Insert into feeder; ensure no twists or tangles
Adjust feed tension until yarn feeds freely
C. Thread Feeder for Patterns
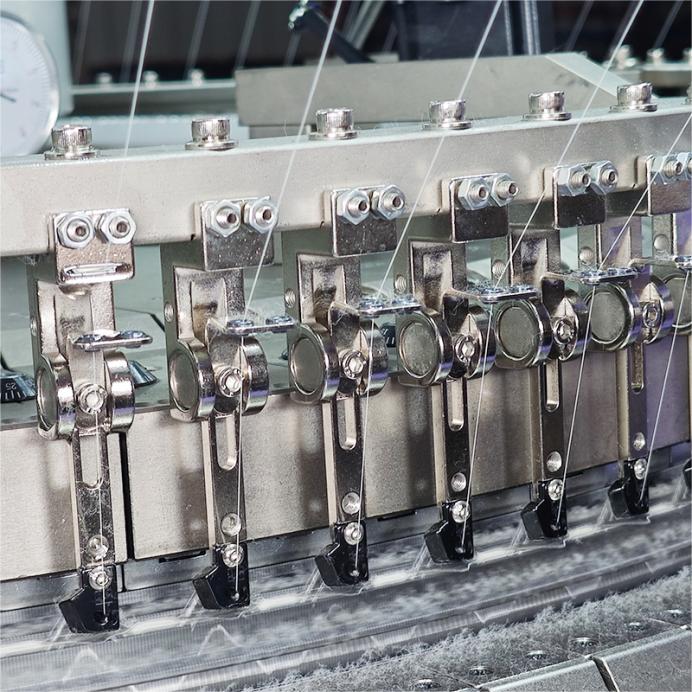

For stripes or colorwork: load additional yarns into secondary feeders
For rib: use two feeders and set gauge accordingly
D. Lubricate Moving Parts
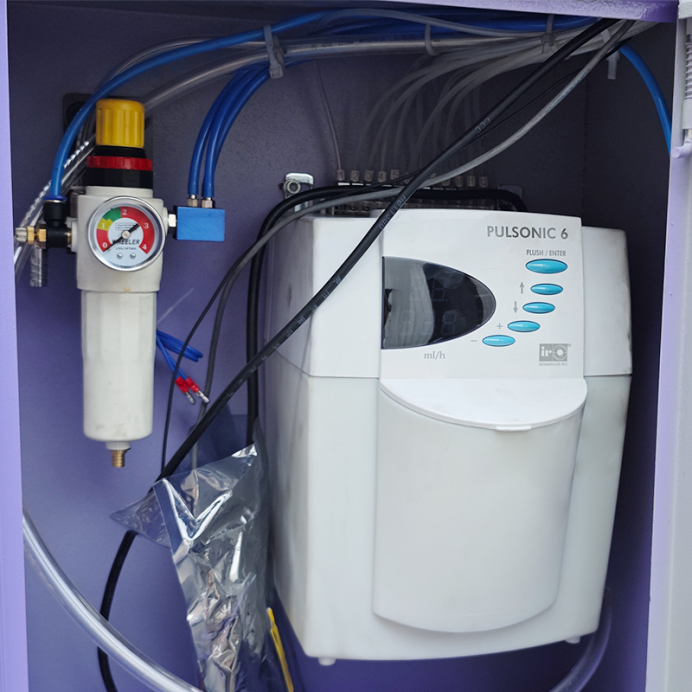

Apply ISO VG22 or VG32 oil to cams and springs weekly
Clean lint and dust before reapplying lubricant
4. Creating a Test Swatch
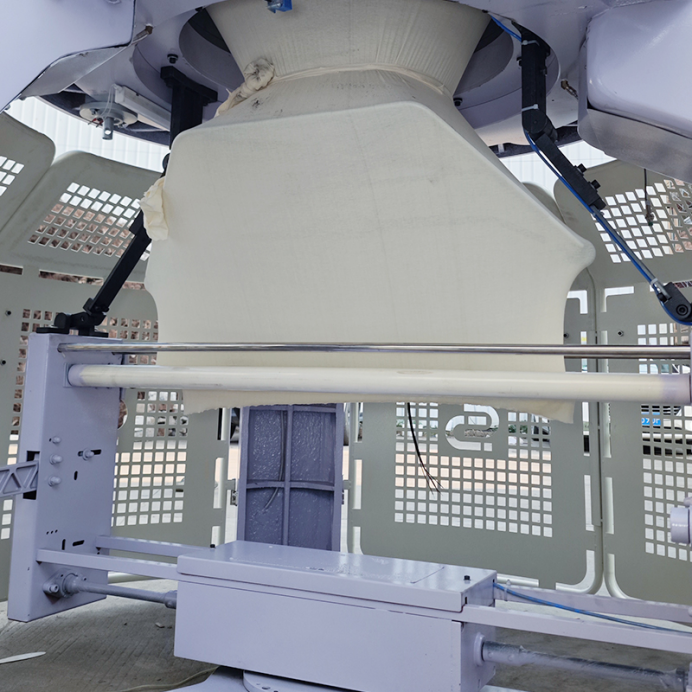
Before launching into production:
Knit about 100 rows at medium speed (600-800 RPM)
Observe:
Stitch formation — any dropped loops?
Stretch & recovery — does it snap back?
Fabric width/length per row — check gauge
Adjust tension + RPM if:
Stitches look loose/tight
Yarn breaks or stretches under tension
Internal Link Tip: Read How to Troubleshoot Knitting Defects for fixes
5. Knitting Full Pieces
Once your swatch passes inspection:
Set desired row count for item length
Beanies: ~160–200 rows
Tubes/scarf blanks: 400+ rows
Start automated cycle
Monitor every 15–30 minutes for missed loops, yarn break, or tension drift
Stop and collect fabric once complete; cut and secure edge
6. Finishing and Crowning
Circular knit (https://www.eastinoknittingmachine.com/products/)items usually lack a top closure:
Use a band saw or hand cutter to open tube
Thread tail through crown stitches with yarn needle
Pull tight; secure with 3–4 small back stitches
Add trims like pom-poms, ear flaps, or labels at this stage
7. Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Daily
Clean yarn feed temp, tension disks, and take down units
Check for needle burrs or rough spots
Weekly
Oil cams, springs, and take-down rollers
Test RPM calibration
Monthly
Replace worn needles and sinkers
Realign cylinder if fabric shows narrowing
Fixing Common Issues
|
Problem |
Cause and Solution |
| Dropped stitches | Bent needles or incorrect tension |
| Yarn breakage | Sharp tip, too much RPM, poor-quality yarn |
| Uneven loops | Misthreaded feeder or cylinder misalignment |
| Fabric twist | Improper take-down tension or flawed roller |
8. Scaling and Efficiency
Interested in going pro?
A. Run Multiple Machines
Set up identical machines for different styles to minimize changeover.
B. Track Production Data
Keep records: RPM, row count, tension settings, swatch results. Monitor consistency across runs.
C. Part Inventory
Maintain spare parts on-hand—needles, sinkers, o-rings—to avoid downtime.
D. Train Staff or Operators
Ensure coverage in case of machine issues or staff availability gaps
9. Selling Your Knitted Items
Want to turn stitches into sales?
Branding: Sew in care labels (machine-washable), size tags
Online Listings: SEO-friendly titles like “Hand-knitted circular knit beanie”
Bundling: Offer sets—hats + scarves for $35–$50
Wholesale: Send to local shops or craft co-ops
Conclusion
Learning how to use a circular knitting machine(https://www.eastinoknittingmachine.com/products/) transforms ideas into tangible products. With the right gauge, yarn, and setup—plus disciplined maintenance—you’re ready to create professional-grade items at scale.
Post time: Jul-09-2025

